Forex Education Trading Method Trading Motivation

Deaching of the great explorer of the truth the builder

More than 50% of the trading volume in Forex is contributed by the interbank market.
This percentage and the talk that surrounds the participation of banks in the forex market are bound to make one wonder about this whole phenomenon.
This piece will hopefully put some of the curiosity around the interbank market to rest.
We are going to touch upon all the main aspects of interbank trading and also discuss the further types within the category of these huge forex players.
Let’s start at the beginning.
What is the Interbank Market?
The interbank market is a trading network that comprises of banks and big trading institutions.
Through this network, banks trade with each other and with some big fund managing institutions and organizations. Banks also trade on behalf of their clients.
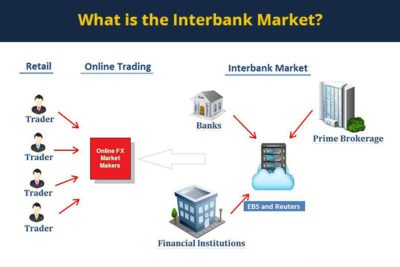
As stated above, the interbank market contributes more than half of the volume to the forex market daily. By extension then this also goes to show that banks are the biggest market makers in forex.
Forex as a decentralized market
In all other kinds of trading there is always a center, a place where all trades can be traced back to. This center will then also be the main market maker and regulatory body.
That’s not how it is with forex though. There is no regulatory authority. This means that there is not one market maker here but many. In reality, all the participants of the market together drive the price up or down.

The more volume a group contributes the more influence they have on the market. This then means that the interbank market is the main market maker.
Now let us take a look at the types of banks that participate in this market and the kinds of trading they indulge in.
Types of banks that participate in Forex
The main organizations constituting the interbank market are:

Central banks trade on behalf of governments. They do it to stabilize their currency and to manage their foreign reserves.
The private and commercial banks trade mainly on behalf of their clients. They take on big investors and clients and have them invest their money with them. The deal is that they will trade the client’s money for them and make profits. This is then achieved often through the interbank market, especially where the investment is big.
Investment managers do the same thing.
Accessing the interbank market
The trades that take place in the interbank market are not like the ones the average retail trader makes. They are much bigger usually made up of millions. Therefore, there is no place for a smaller level trader looking to invest smaller amounts in forex in the interbank network.
There is no use trying to access it for trading purpose.
However, information about ask and bid prices can prove to be valuable. As discussed before, banks are the biggest market makers. Knowing their interbank market sentiment can therefore really inform the trader about the possible turns the market is bound to take.

For this reason, for the sake of information you can look into sources that claim to offer insider information.
For the longest time, forex was not open to the retail trader. In fact, it only became possible for individual traders to participate in the market after 1990s. Before this, only banks used to trade currency.
The minimum amount of currency traded at those times was in millions, which is why it was inaccessible to the common man.
While the market has now been opened to retail traders now, that market continues to exist and flourish in which millions or billions are traded. One reason why this is possible is that a lot of this happens on credit base because these banks have long term trading relations with each other.
The interbank market, therefore, is fascinating to read about and learn from, but it is no place for individual traders.
We hope this piece proved to be useful and you were able to learn a bit more about the interbank market and its role in forex trading.
Let us know if you want us to cover any specific topics next.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
Fine jewelry, watches and giftware will almost certainly attracts you...
Leave A Comment